Trump's Tariffs Bomb: A Timeline Of Global Trade War 2.0 With Markets Ebb And Flow
U.S. President Donald Trump reignited the old flames of tariffs when he returned to the White House with a bang early this year. What started as campaign promises quickly turned into a full-blown global trade war. Trump's tariff saga has shaken markets across the globe. From Canada to China to India - he spared no one. In retaliation, the largest economy of the world was hit by several tariffs.
Below is the complete timeline of what happened in the last 125 days since Trump regained power as the President of the United States.
January 20, 2025: Trump Sworn In, Promises Tariffs
Donald Trump was sworn in as U.S. President again, and from the very first day, he was clear that foreign countries would pay up. He vowed to slap tariffs on countries like Mexico, Canada, and China to protect American jobs and businesses.
February 1: Official Tariff Orders on Mexico, Canada, and China
Trump signed an executive order under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA), imposing 10% tariffs on all Chinese imports along with the existing tariffs of up to 25% on many Chinese goods and 25% tariffs on imports from Mexico and Canada, barring Canadian oil and energy exports. These tariffs were supposed to come into effect on 4th February.
February 3 to 4: Temporary Pause and China's Counterattack
Trump's decision met with sharp criticism and threats of retaliation from all three countries. Justin Trudeau, the then PM of Canada, said they would file a 25% retaliatory tariff on American goods like liquor, vegetables, clothing, shoes, and perfume etc. Trump agreed to a 30-day pause on tariffs against Mexico and Canada as both countries promised to improve border security.
However, on February 4, 10% tariffs on Chinese goods took effect. China quickly retaliated by imposing 15% tariffs on U.S. coal, liquefied natural gas, crude oil, agricultural machinery, and vehicles.
February 10 to 13: Tariff Imposed On Steel and Aluminum Imports
Donald Trump announced plans to raise tariffs on steel and aluminum imports to 25%, removing previous exemptions for some countries, which were expected to come into effect on March 12.
He also unveiled plans for "reciprocal tariffs" to match tariffs imposed by other countries on U.S. goods. Economists warned this could disrupt decades of trade rules and create chaos. Later, Trump gave some countries, like Canada, Mexico, and Brazil, special permission to avoid the extra import taxes.
March 4 to 6: Tariffs Take Effect and Auto Industry Exemptions
On March 4th, the 25% tariffs on Canada and Mexico came into force, with a 10% limit on Canadian energy imports. Post this, Canada and Mexico promised retaliatory tariffs on the US.
The tariffs on Chinese goods doubled to 20%. China imposed 15% tariffs on U.S. farm products, including pork, soybeans, and beef.
Trump exempted U.S. automakers from some tariffs on Mexican and Canadian goods temporarily after discussions with automaker leaders.
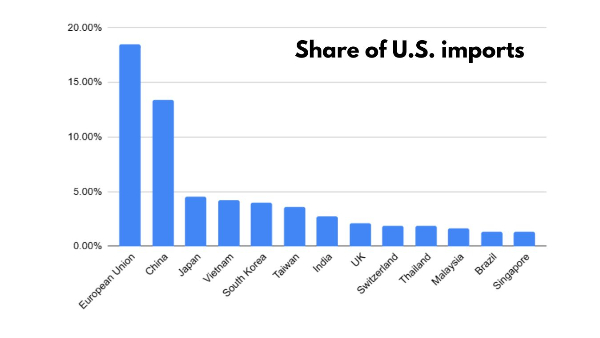
March 10 to 12: China and EU Retaliate Further
China's 15% tariffs on key American farm exports began on March 10th. Trump's 25% steel and aluminium tariffs also took effect. The European Union announced retaliatory tariffs on USD 28 billion worth of U.S. goods, including textiles, bourbon, motorcycles, and peanut butter. Canada planned additional retaliatory tariffs worth USD 20.7 billion.
March 13: Trump Threatens 200% Tariff on European Wine
In retaliation to the EU's tariff plans, Trump threatened a massive 200% tariff on European wine, Champagne, and spirits.
March 24 to 26: New Tariffs on Venezuela and Auto Imports
Trump announced 25% tariffs on imports from countries buying oil or gas from Venezuela. On March 26, he announced 25% tariffs on imported automobiles starting April 3, which escalated the trade conflict further. The trade rules further came into effect from.
April 2 to 5: Reciprocal Tariffs Go Live
Starting April 5th, Trump implemented his "reciprocal tariffs", with a baseline 10% tariff on almost all imports. Higher tariffs targeted countries with trade surpluses where a tariff of 24% was imposed on Japan, 34% on China, 20% on the EU. Canada and Mexico could still send USMCA-compliant goods tariff-free. China matched with a 34% tariff on U.S. products.
Electronics, including smartphones and laptops, were temporarily exempt from tariffs, but further tariffs on semiconductors were under investigation.
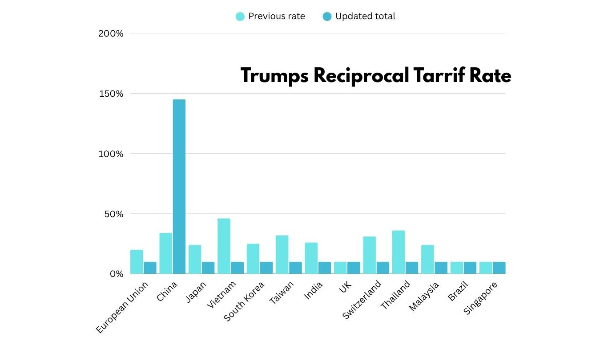
April 9 to14: Tariff Escalation and Investigations
Trump's higher reciprocal tariffs officially began but were quickly suspended for 90 days except for China, which saw tariffs increase to a whopping 125%. The EU delayed retaliatory tariffs for 90 days, hoping to negotiate.
Canada implemented a 25% tariff on non-compliant auto imports. Trump hinted at temporarily exempting the auto industry to ease supply chain pressures.
April 29: Auto Tariffs Adjusted
Trump relaxed some auto tariffs for vehicles assembled in the U.S. with foreign parts, offering rebates to encourage domestic assembly.
May 3 to 4: Auto Tariffs Expand; Film Industry Targeted
Additional 25% tariffs on imported auto parts went into effect. Trump threatened 100% tariffs on foreign films, claiming the U.S. movie industry was suffering.
May 8: US-UK Trade Deal and EU Threat
The U.S. and UK agreed on a trade deal reducing tariffs on UK cars and steel, with the UK buying more American beef and ethanol. The EU announced plans to take the U.S. to the World Trade Organisation over reciprocal tariffs.
May 12: Temporary Truce with China
After months of trade battles, the U.S. and China agreed to roll back most tariffs and declared a 90-day grace period. The U.S. cut its tariff rate on Chinese goods from 145% to 30%, to which China responded by chopping its tariffs on U.S. products from 125% to 10%. Wall Street reacted early to this news, and gains were seen in all three major indices.
May 23 to 25: Apple and EU Under Pressure
As of the most recent move, Donald Trump threatened to impose a 25% tariff on Apple products unless iPhones were made in the U.S. The tariff could be coming as soon as the end of June.
He also announced a 50% tariff on all EU imports starting June 1, later delaying it to July 9 after talks with the EU Commission President, Ursula von der Leyen.
.
.
.
(GoodReturns team will update this article every time there is a headline development)



 Click it and Unblock the Notifications
Click it and Unblock the Notifications